There are three types of heat transfer: convection, conduction, and radiation.
Convection: Thermal waves caused by the movement of fluid materials such as heated gases or liquids with thermal energy
Conduction: Heat is transferred from the high temperature part to the low temperature part in order.
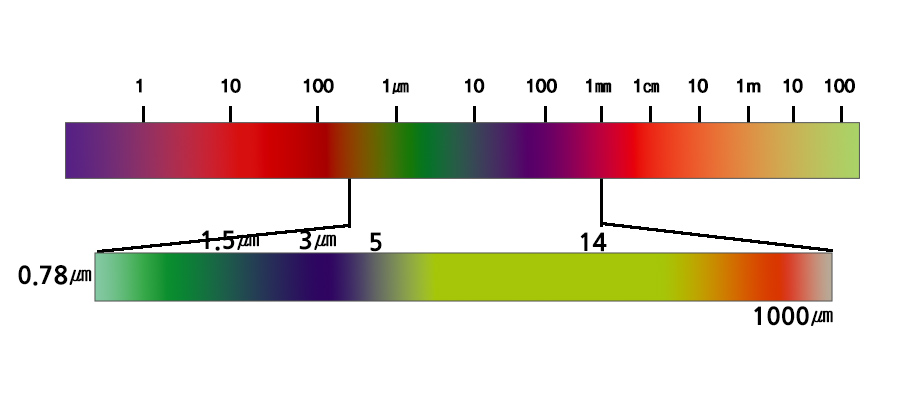
Radiation: When the sun is covered in grime, heat is cut off at the same time as sunlight, this is how it is transferred to heat in the same way as light (electromagnetic waves with longer wavelengths than visible light, i.e., infrared radiation)
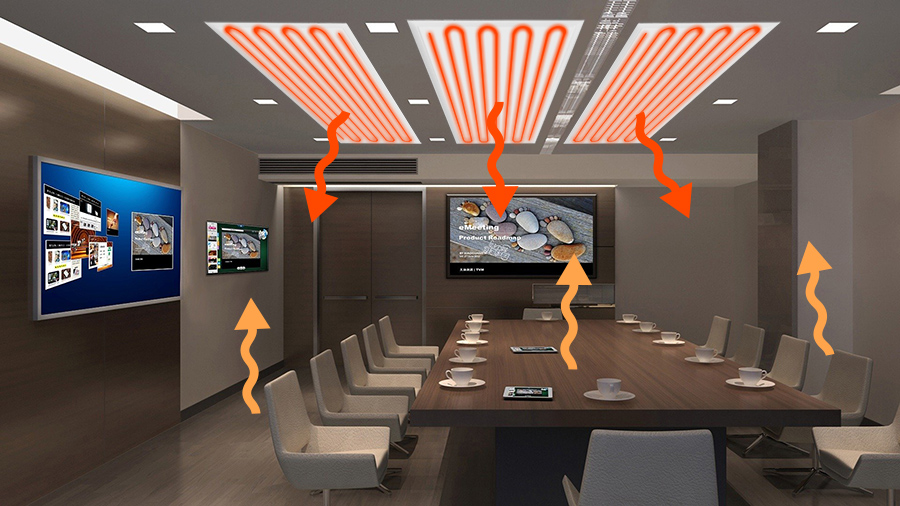
Ceiling radiant heating heats the space to a pleasant temperature as a whole. Ceiling radiant heating is a surface heating method that emits heat using the entire surface. Unlike electric radiators, it heats the room with cozy radiant heat. There is very little convection. Radiation transfers heat through infrared radiation. Radiant heat radiates like the sun. The light spreads at right angles to the surface. In other words, ceiling radiant heating spreads heat from top to bottom. When infrared wavelengths hit hard objects such as furniture, floors, and human bodies, they are converted into heat. Solid objects release energy absorbed into the room as heat.

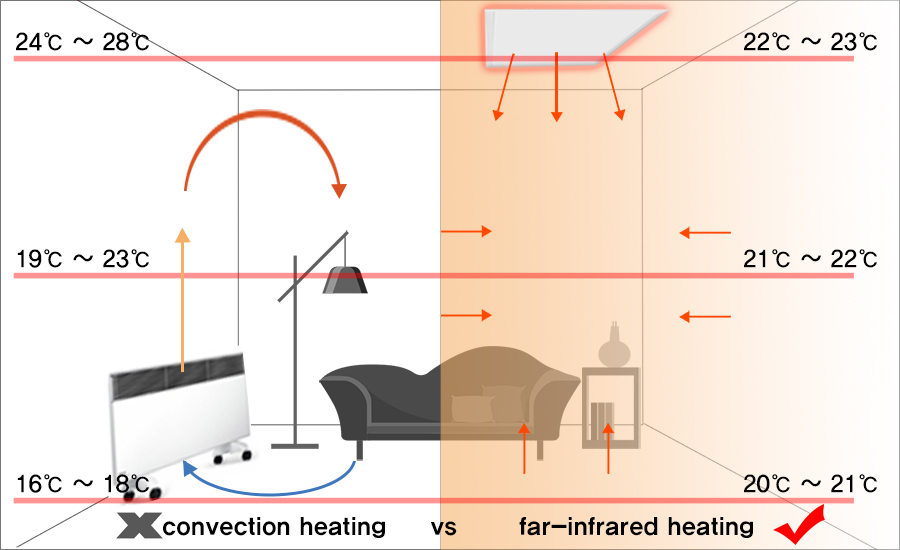
Convection heating works by heating the air itself. Conventional hot air heaters tend to distribute heat unevenly because air must circulate to warm the entire room.
Because convection heating only affects the surrounding air, people tend to get closer to heaters to feel the benefits. Therefore, warmth may be limited on the far side of the heater or on the lower part of the room.
Unlike convection heating, far-infrared radiation heating directly heats the body and object in contact by emitting radiant heat. This heat is released back into the room or space, so that the heat is evenly distributed.
Sunway's far-infrared heating technology does not rely on warm air circulation. So, even if you leave your doors or windows open on a cold day, you can feel the direct far-infrared heat as if you were feeling the warm sunshine on a winter day.
Better heat distribution. Far-infrared heating evenly distributes heating, resulting in less temperature difference. Fast heating time. As soon as the heater is turned on by applying a far-infrared heating plate, the effect appears. Reducing heating costs Running far-infrared heat panels is more cost-effective than conventional convection heaters. High-quality heating. Convection heaters heat the air and move it around. Far-infrared rays do not heat the air directly. Far-infrared heat provides a feeling of health and well-being that conventional vector heaters cannot provide. Many users compare the effects of far-infrared heat to something similar to sunlight. Easy installation. Far-infrared heating plates can be attached to the ceiling or wall, making it as easy and simple as installing LED lights. Minimalist design. Far-infrared heating panel design is simple yet eye-pleasing. Automatic operation. No buzzing, no buzzing, no creaking or rattling. The far-infrared thermal panels work quietly. Low maintenance: Far-infrared heating systems have no moving or motor parts, so little maintenance is required. There are also no filters or fans that need cleaning or replacement.